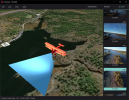
DJI advertises the Field of View (FOV) of their lenses using the diagonal angle. This FOV value corresponds to an aspect ratio of 4x3.
It is sometimes desired to know either the horizontal FOV or vertical FOV or both. To compute either the horizontal or vertical FOV it is tempting to use the Pythagorean Theorem to compute the ratio of aspect-horizontal to aspect-diagonal and then multiply the diagonal FOV by that ratio to obtain the horizontal FOV but that would be incorrect. This method can be summarized as follows:
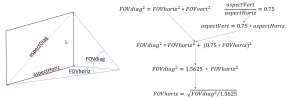
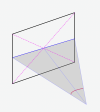
The reason the above method would be incorrect is because the FOV angle, when projected onto a flat plane has a non-linear relationship with distances along that plane. For example, a one-degree change of FOV when the FOV is small results in a relatively small linear change on that flat plane. However, a one-degree change of FOV when the FOV is large (closer to 180) yields a massive change on that same flat plane.
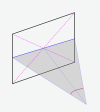
As a result, the ratio of aspect-horizontal (or vertical) to aspect-diagonal must be compared to the ratio of tangents of the half FOV angles. This method can be summarized as shown below:
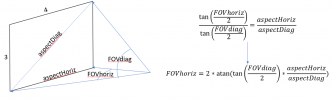
The above method is also summarized here:
 medium.com
medium.com
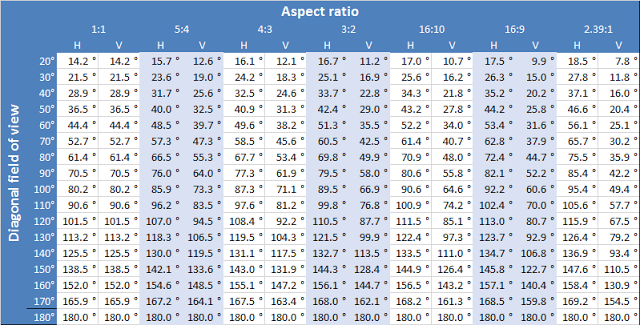
Using this method I can successfully duplicate the example values provided in the link above.
Occasionally, I see FOV values and their horizontal equivalents posted in this forum. However, the values posted do not match those from this formula. Can anyone who is familiar with this conversion provide any details about the method they use to convert the diagonal FOV to horizontal and vertical values?
It is sometimes desired to know either the horizontal FOV or vertical FOV or both. To compute either the horizontal or vertical FOV it is tempting to use the Pythagorean Theorem to compute the ratio of aspect-horizontal to aspect-diagonal and then multiply the diagonal FOV by that ratio to obtain the horizontal FOV but that would be incorrect. This method can be summarized as follows:

The reason the above method would be incorrect is because the FOV angle, when projected onto a flat plane has a non-linear relationship with distances along that plane. For example, a one-degree change of FOV when the FOV is small results in a relatively small linear change on that flat plane. However, a one-degree change of FOV when the FOV is large (closer to 180) yields a massive change on that same flat plane.
As a result, the ratio of aspect-horizontal (or vertical) to aspect-diagonal must be compared to the ratio of tangents of the half FOV angles. This method can be summarized as shown below:

The above method is also summarized here:

Converting diagonal field of view and aspect ratio to horizontal and vertical field of view
Converting diagonal field of view and aspect ratio to horizontal and vertical field of view Note: this post was refined on Apr 23, 2016 to reflect a more accurate method of calculation. Continuing …
Using this method I can successfully duplicate the example values provided in the link above.
Occasionally, I see FOV values and their horizontal equivalents posted in this forum. However, the values posted do not match those from this formula. Can anyone who is familiar with this conversion provide any details about the method they use to convert the diagonal FOV to horizontal and vertical values?