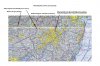
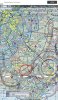
1. What are the light blue lines - There are air traffic routes that cross the Class B lines. There is also dashed blue circle in the same area - Class D airspace
2. Solid magenta circle
What does the Mode C / 30 NM circle on a Sectional Chart mean?
The Mode C ‘veil’ does NOT apply to sUAS operations, so no need for drone pilots to worry about this.
Here is an excerpt from the Aeronautical Information Manual, page 133, for more context about how the Mode C veil applies to manned aircraft operations:
The airspace within 30 nautical miles of an airport listed in Appendix D, Section 1 of 14 CFR Part 91 (generally primary airports within Class B airspace areas), from the surface upward to 10,000 feet MSL. Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, aircraft operating within this airspace must be equipped with automatic pressure altitude reporting equipment having Mode C capability.
However, an aircraft that was not originally certificated with an engine−driven electrical system or which has not subsequently been certified with a system installed may conduct operations within a Mode C veil provided the aircraft remains outside Class A, B or C airspace; and below the altitude of the ceiling of a Class B or Class C airspace area designated for an airport or 10,000 feet MSL, whichever is lower.
3. Gray border
In United States
aviation, a
terminal radar service area (
TRSA) is a delimited airspace where
radar and
air traffic control services are made available to pilots flying under
instrument flight rules or (optionally)
visual flight rules, to maintain aircraft separation.
TRSAs most often surround busy U.S. airports. In recent years, many of them have been replaced by
Class C or
Class B airspace.[
citation needed]
Terminal Radar Service Area was established as part of a program to create terminal radar stations at selected airports. Because they were not subject to the rulemaking process of 14 CFR Part 91, they do not fit into any existing U.S. classifications of airspace, and have been classified as non-part 71 airspaces. While operating in these airspaces, pilots who choose to participate receive radar services, but participation is not required for VFR operations.
TRSAs encompass a primary airport with a class "D" designation, with the TRSA above other controlled airspace (Typically Class E Airspace) with a typical floor of 700 feet or 1,200 feet AGL (Above Ground Level).
TRSAs are shown on most VFR (Visual Flight Rules) sectional charts
as solid black/gray.