web crawling spiders aka robots.
Wikipedia
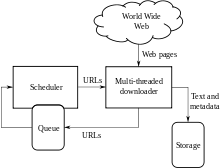
Architecture of a Web crawler
A
Web crawler, sometimes called a
spider, is an
Internet bot that systematically browses the
World Wide Web, typically for the purpose of
Web indexing (
web spidering).
Web search engines and some other sites use Web crawling or spidering software to update their
web content or indices of others sites' web content. Web crawlers copy pages for processing by a search engine which
indexes the downloaded pages so users can search more efficiently.
Crawlers consume resources on visited systems and often visit sites without approval. Issues of schedule, load, and "politeness" come into play when large collections of pages are accessed. Mechanisms exist for public sites not wishing to be crawled to make this known to the crawling agent. For instance, including a
robots.txt file can request
bots to index only parts of a
website, or nothing at all.
The number of Internet pages is extremely large; even the largest crawlers fall short of making a complete index. For this reason, search engines struggled to give relevant search results in the early years of the World Wide Web, before 2000. Today relevant results are given almost instantly.
Crawlers can validate
hyperlinks and
HTML code. They can also be used for
web scraping (see also
data-driven programming).


